What we often dismiss as “just smog” is now one of the leading causes of chronic inflammation, cardiovascular strain, respiratory decline, and, increasingly, premature death across India. The uncomfortable truth is this: Air pollution isn’t seasonal, and it isn’t harmless — it’s silently shortening lives.

Cities across the country — including Delhi, Mumbai, NCR, Punjab, Lucknow, Kolkata, and more — spend weeks in hazardous AQI zones, leaving millions unsure of how much air quality is good for their health or why routine coughs, breathlessness, fatigue, and sinus issues have suddenly become a part of daily life.
The reality is that death by air pollution has become a measurable, scientifically documented public health threat.
To understand the profound impact of air pollution on human health, our team conducted an extensive meta-analysis over the past year, bringing together India-specific findings, global cohort data, disease mapping, longitudinal research, and region-specific evidence studies on air pollution and premature death.
What emerged was alarming, but also empowering: with awareness and the right strategies, individuals and families can protect themselves.
Here, we break down the science, the research, the realities of living with toxic air, and most importantly, the practical steps you can take today to safeguard your lungs, your heart, your family, and your future.
Luke’s Stand Against Toxic Air –Why This is A Health Emergency
For Team Luke, the conversation around air pollution has never been about inconvenience — it has always been about life, longevity, and human dignity. Clean air isn’t a wellness trend; it’s the first pillar and a non-negotiable component of survival.
Without clean air, the body stays inflamed, the lungs stay burdened, the heart works harder, immunity drops, and the risk of premature death increases multifold.
This is why Luke has consistently taken a public, vocal, and uncompromising stand on this issue.
Luke’s Advocacy Includes:
- Initiating a petition demanding stricter air-quality regulations
- Educating millions through videos, blogs, and social platforms on how toxic air affects every cell
- Working with environmental bodies and health experts to highlight the connection between chronic disease and polluted air
- Filing a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the Supreme Court of India, urging systemic changes and responsible action
Team Luke’s message has remained consistent across every platform:
“If the air we breathe is toxic, no nutrition plan, fitness routine, supplement, or medication can offset the continuous internal damage. Clean air is the foundation upon which good health stands.”
From children with asthma to adults facing unexplained heart palpitations, from rising COPD cases to younger individuals experiencing heart attacks, the air pollution impact on human health is visible in every consultation room.
And behind many of these cases lies the same silent driver: chronic exposure to polluted air leading to early mortality.
Team Luke’s stand is not against a system; it is for the people, for families, for future generations who deserve lungs that are not fighting for breath every single day. Luke’s advocacy is rooted in the belief that clean air should not be a luxury available to a few; it should be a birthright available to all.
You can also be part of the change: Click here to know more.
Understanding the Impact of Air Pollution on Human Health
Air pollution in India is not a single pollutant problem — it is a complex chemical soup that directly attacks the lungs, heart, blood vessels, and brain. The danger lies not only in what we inhale, but how deeply these particles penetrate the body, creating a perfect storm for death by air pollution.
Below is a simplified breakdown of the most harmful pollutants and what they do inside the human body.
The Pollutants: A Quick Breakdown
These pollutants aren’t merely irritants — they are biochemically active toxins with the power to alter human physiology at the most fundamental level.
| PM2.5 and PM10 (Particulate Matter) | Nitrogen Oxides (NO₂ and NOx) | Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) |
India’s PM2.5 levels remain far above WHO guidelines, with 100% of 1.4 billion Indians exposed to unsafe levels — a major pathway toward air pollution and premature death. |
|
|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | TVOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) |
Colorless, odorless, deadly.
|
Often an indoor threat.
|
What Do These Pollutants Do Inside the Body?
They Bypass the Body’s Natural Defenses
Fine particulate matter (especially PM2.5) crosses:
- Nasal defenses
- Mucosal barriers
- Alveolar membranes
Once inside the bloodstream, these particles act like micro-invaders, triggering the same inflammation seen in chronic diseases.
What science says:
- PM2.5 particles activate TLR4 receptors, triggering systemic inflammation
- They generate excess ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) → oxidative stress
- They impair mitochondrial function → poor cellular energy
- They disrupt endothelial nitric oxide → vascular stiffness

Result: Cells age faster, blood vessels stiffen, and organs lose resilience — setting the stage for premature death.
Support your body’s natural detox pathways.
👉 Explore The Lymphatic Reset Course to improve immunity, skin health, and overall wellness.
They Damage the Cardiovascular System (the #1 pathway to premature death)
Air pollution acts exactly like chronic smoking, even in non-smokers.
Specific biological effects:
- Endothelial injury → plaque formation
- Increased blood viscosity → clot formation
- Autonomic imbalance → arrhythmias
- Vasoconstriction → elevated blood pressure
Here’s what science:
- Increased IL-6, TNF-α → heightened inflammatory burden
- Higher fibrinogen levels → increased stroke and heart attack risk
- Accelerated atherosclerosis even in young individuals

This is why cardiologists across India now consider polluted-air exposure a major independent risk factor for heart attacks, even among people under 40.
They Disrupt Lung Health
The pollutants:
- destroy alveolar walls
- reduce lung elasticity
- impair gas exchange
- increase airway hyperreactivity
Chronic exposure causes:
- decreased lung capacity
- COPD-like changes even in non-smokers
- persistent cough, wheezing, chronic bronchitis
- lung cancer
This damage is irreversible, especially in children.
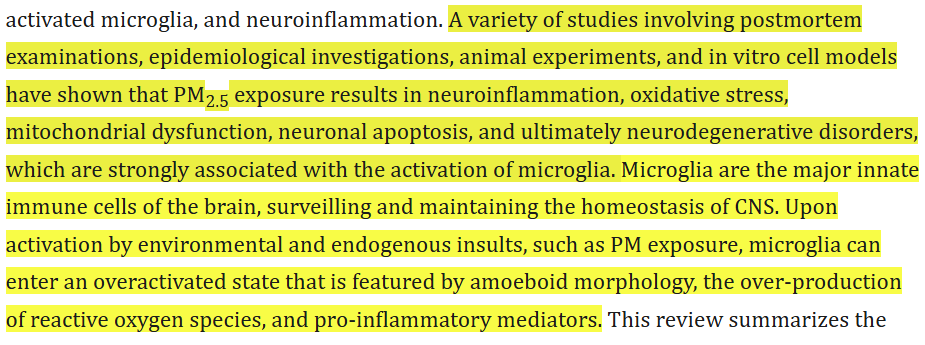
They Alter Brain Function
What enters the lungs does not stay in the lungs. Fine particles migrate to the brain through the bloodstream and, in some cases, directly through the olfactory nerve.
Inside the brain, pollutants:
- trigger microglial activation (immune cells of the brain)
- increase oxidative stress
- damage the blood–brain barrier
- reduce oxygenation
- cause microvascular inflammation
Over time, this leads to:
- reduced memory precision
- mood instability
- slowed processing speed
- higher risk of neurodegeneration
- impaired emotional regulation
Want to know more about the impact of air pollution on the brain? Click here.
They Trigger Chronic Systemic Inflammation
This is the silent, underlying mechanism behind most pollution-associated diseases.
Chronic exposure elevates inflammatory markers like:
- CRP
- IL-6
- TNF-α
- ROS
This systemic inflammatory environment accelerates biological ageing, destabilizes metabolic balance, impairs immune function, and damages blood vessels.
Over months and years, this inflammatory burden increases the risk of:
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune disorders
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Stroke
- Cancer
This is why foundational medicine views air pollution as not just an environmental crisis but a deep metabolic and inflammatory crisis, tightly linked to premature death.
How Air Pollution Ultimately Causes Premature Death
Premature death from air pollution doesn’t occur due to a single event. It is the cumulative impact of chronic inflammation, vascular injury, impaired oxygenation, and cellular stress that gradually weakens the body until a critical system fails — usually the heart, brain, or lungs. Below are the primary biological pathways through which polluted air shortens life expectancy in India.
Cardiovascular Events — The Leading Cause of Death
Air pollution thickens the blood, stiffens arteries, and heightens clotting. When a plaque becomes unstable — often triggered by inflammation — it can rupture, causing sudden:
- myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- fatal arrhythmia
- heart failure
This is the biggest driver of death by air pollution worldwide and in India.
Respiratory Failure
Damaged alveoli, chronic bronchitis, COPD-like airway remodeling, and reduced lung function can lead to:
- chronic hypoxia
- respiratory infections
- acute respiratory distress
- long-term decline in breathing capacity
For the elderly, children, and people with asthma, pneumonia, or weak lung tissue, this can be life-threatening.
Stroke and Cerebrovascular Collapse
Pollutants inflame cerebral vessels, increase clotting, impair oxygen delivery, and elevate oxidative stress. This dramatically raises the risk of:
- ischemic stroke
- hemorrhagic stroke
- transient ischemic attacks
The link between PM2.5 and acute stroke events is now one of the strongest in medical literature.
Accelerated Cellular Ageing
PM2.5 shortens telomeres, damages DNA, and impairs mitochondrial resilience.
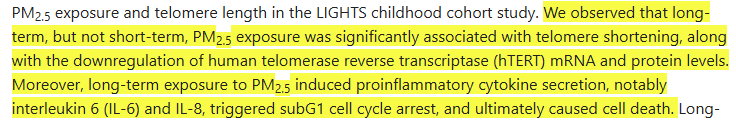
Shorter telomeres → faster ageing → higher susceptibility to disease → earlier mortality.
This is a direct, biological explanation for air pollution and premature death.
Cancer Pathways
Carcinogenic pollutants (benzene PM-bound toxins) penetrate deep tissues and:
- damage DNA
- trigger mutations
- impair immune surveillance
- activate oncogenes
This explains the rise in lung cancer among non-smokers in polluted Indian cities like Delhi and Mumbai.
Take control of your cancer journey with expert guidance and holistic support.
👉 Join Cancer Care Program with Luke’s Team to receive personalised care.
Multigenerational Impact
Pollution harms fetal development, disrupts placental function, and increases neonatal disease. Children start life with compromised lung capacity, higher inflammation, and increased vulnerability — setting the stage for long-term illness and early mortality.
What Our Meta-Analysis Reveals About India’s Air Pollution Crisis
Over the past year, our team conducted an extensive meta-analysis on the Air Pollution Crisis and Its Effects on Public Health in India. And what emerged from this comprehensive review is both urgent.
Vulnerable Populations
Groups facing the highest health risks:
- Children (stunted lung growth, ADHD risk, irreversible lung damage)
- Pregnant women & infants (low birth weight, neonatal disease)
- Elderly adults (stroke, COPD, heart disease)
- Marginalised women (household pollution)
- Residents near industrial zones
- Low-income and informal settlement communities
- People with pre-existing conditions
- Pets (confirmed rise in respiratory issues in several Indian cities)
City-wise Snapshot (as of September 2025)
| City | AQI Status | Primary Concern |
| Delhi | 115+ (Poor–Hazardous) | PM2.5, PM10, NOx |
| Kolkata | 92 (Poor) | PM2.5, cardiac risks rising |
| Mumbai | 66–120 (Moderate–Poor) | PM10, respiratory issues |
| Ahmedabad | 61+ (Moderate–Poor) | PM2.5/PM10, COPD in non-smokers |
| Pune | 67+ (Moderate) | PM10, child & elderly vulnerability |
| Chennai | 58–63 (Moderate) | Industrial SO₂ & PM exposure |
| Hyderabad | 39+ (Variable) | Stunted lung growth in children |
| Bangalore | 58 (Moderate) | Local NO₂ hotspots |
Global Research about Air Pollution and Premature Death
While India’s crisis is severe, the connection between air pollution and premature death has been proven repeatedly across global scientific literature.
One of the most widely cited analyses comes from The Lancet Planetary Health (2021), which evaluated PM2.5 and NO₂ exposure across 969 European cities.
- Despite Europe having far tighter regulations and cleaner air compared to India, researchers found that simply meeting the recommended limits could prevent over 50,000 premature deaths every year.
- Reducing pollution to the lowest observed levels would more than double that benefit.
- The most important takeaway for India is this: even small reductions in PM2.5 dramatically extend lifespan, a pattern seen repeatedly across global datasets.
A second landmark study, published in Nature Communications (2021), examined pollution-related mortality across 199 countries, focusing on consumption within the G20 nations.
- The numbers were staggering: 1.98 million premature deaths linked to PM2.5 in a single year, with India accounting for nearly half a million of them.
- What makes this study unique is that it showed how pollution deaths are not only caused locally — they are tied to global production, industrial patterns, and the cross-border movement of pollutants.
- The average age of death was just 67 years, reinforcing how deeply pollution erodes healthy lifespan.
In Poland, another 2023 study from Atmospheric Environment showed that even in a country with consistent monitoring and stricter emission controls, 6700 premature deaths over five years were directly attributable to PM2.5, PM10, NO₂, and ozone.
- The pattern was identical to India’s: cardiovascular deaths dominated, followed by respiratory failure — the same biological pathways we see in Indian patients exposed to chronic pollution.
A global-scale mortality model published in Nature (2015) further strengthened the evidence.
- By simulating PM2.5 and ozone exposure across continents, the researchers concluded that 3.3 million deaths every year were attributable to outdoor air pollution — a number projected to double by 2050 if no major interventions are implemented.
- Importantly, the model identified residential energy use (cooking, heating, biomass fuels) as the single biggest contributor in India and China — mirroring India’s continued struggle with indoor and outdoor pollution overlap.
Finally, a pivotal JAMA (2017) study analyzing millions of older adults in the United States established one of the most critical findings in air pollution science: there is no safe threshold.
- Even pollution levels below U.S. national standards increased daily mortality.
- A 10 μg/m³ rise in PM2.5 increased deaths by 1.05% in just 24 hours, proving how extremely sensitive the human body is to particulate burden — especially in vulnerable groups.
Across all five studies, conducted in vastly different settings, the message is unequivocal:
- PM2.5 is the most dangerous pollutant
- Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pollution-related death
- Pollution shortens life expectancy in measurable, predictable ways
- Reductions in PM2.5 directly increase lifespan
- There is no safe level of exposure
Together, these studies strengthen the scientific backbone of what India is experiencing in real time: a rising wave of air pollution and premature death, driven by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, vascular injury, and multi-organ decline.
Protecting Yourself From Air Pollution — Practical, Science-Backed Approaches
When the outside air becomes a daily threat, the most powerful question you can ask is: “What can I do to protect my lifespan and my family’s health today?”
So the first step is always exposure reduction, followed by nutrition, respiratory resilience, and monitoring.
Below is a structured, easy-to-follow protection plan prepared by Luke’s team.
Aggressive Exposure Reduction (The Priority)
No diet, supplement, or lung remedy can offset daily inhalation of polluted air. Peak-exposure reduction is the single strongest intervention scientifically proven to slow lung-function decline and reduce the risk of death by air pollution.
1. Indoor is the New Outdoor
- Track AQI using apps (AQI.in, SAFAR).
- If AQI >150, children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with asthma must remain indoors.
- This dramatically reduces the air pollution impact on human health.
2. Use a True HEPA Air Purifier
- Keep one in the bedroom where you spend 7–9 hours daily.
- Choose HEPA + activated carbon (CADR ≥ 200).
- Shut windows during peak pollution.
- Clean/change filters on time.
| Air Quality Level | How Much Air Quality Is Good for Health? | Action |
| 0–50 (Good) | Safe | Normal outdoor activity |
| 51–100 (Moderate) | Acceptable | Sensitive groups caution |
| 101–150 (Unhealthy for sensitive groups) | Not good for children/elderly | Limit outdoor time |
| >150 (Unhealthy) | Not safe | Stay indoors, purifiers on |
| >300 (Hazardous) | Dangerous — linked to air pollution and premature death | Mask + indoor day |
3. Mask Up Properly
- Only N95/KN95 masks work for PM2.5.
- Surgical masks offer <10% protection.
- Ensure a tight seal around the nose and cheeks.
4. Indoor Detox
- Avoid incense, camphor, chemical candles, and indoor fireworks.
- Wet-dust instead of dry sweeping (prevents recirculating PM).
- No burning leaves or household waste.
5. Stop All Active & Passive Smoke
- Cigarettes, vaping, and passive smoke + polluted air = synergistic lung destruction. This combination accelerates inflammation and increases the risk of premature death.
6. Ventilation Timing
- Ventilate between 12 pm and 4 pm (lowest PM levels).
- Avoid early mornings and late evenings in smog seasons.
The Nutritional Shield
Nutrition cannot eliminate pollution exposure, but it can reduce inflammation, protect lung tissue, and buffer oxidative damage — weakening the pathways that link pollution to premature death.
Foods That Protect the Lungs
Anti-Inflammatory Essentials:
- Spinach, kale, amaranth
- Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage
- Tomatoes, pumpkin, carrots
- Guava, berries, amla, apples
- Garlic, turmeric, ginger, tulsi
- Omega-3 fats (walnuts, flaxseed, sardines)
Food Categories That Work
| Category | Top Picks & Why | Daily Goal |
| Leafy Greens | Vitamin C, E, carotenoids → reduce oxidative lung damage | 1–2 cups |
| Crucifers | Sulforaphane activates lung detox enzymes | 1–2 cups |
| High-antioxidant Fruits | Reduce free radical load from PM2.5 | 2–3 servings |
| Carotenoid Foods | Protect alveoli from inflammation | 1 cup |
| Omega-3 Rich Foods | Reduce cardiovascular stress (big driver of pollution deaths) | Daily nuts/seeds or 2–3 fish servings/week |
Foods That Worsen Inflammation (Limit These)
- Refined sugar & flour
- Deep-fried foods
- Ultra-processed snacks
- Excess salt
- Packaged bakery items
Keeping these <10% of daily calories supports natural healing.
A Tea for Your Lungs For a Lung Cleanse, try this Magic Lung Tea

Disclaimer: Please keep your healthcare provider in the loop before introducing any new food item into your lifestyle, especially if you have a medical condition or are on medications. In case you are allergic to certain foods, please avoid them.
Daily Supportive Practices
- 2–3 L water/day → thins mucus, improves clearance
- Steam inhalation 5 mins → eases inflammation
- Saline nasal rinse → removes PM from nasal passages
- Pranayama indoors (avoid outdoors on high AQI days)
Supplementation
Always under medical guidance — especially for children, seniors, and pregnant women.
| Supplement | Lung/Heart Protection Benefit | Food Sources |
| Vitamin C | Neutralises pollution-derived free radicals | Guava, peppers, kiwi |
| Omega-3 (EPA/DHA) | Lowers inflammation; protects heart from PM-induced stress | Sardines, walnuts, flaxseed |
| Vitamin D | Critical for immunity; pollution worsens deficiency | Egg yolk, mushrooms |
| Vitamin E | Protects lung membranes from oxidative attack | Almonds, sunflower seeds |
| Zinc | Helps tissue repair & mucosal immunity | Seeds, legumes |
Remember: CODE-Z
A simple memory tool for lung defense against PM2.5:
- C – Vitamin C
- O – Omega-3
- D – Vitamin D
- E – Vitamin E
- Z – Zinc
Respiratory Resilience & Monitoring
Your lungs are not passive organs — they can be strengthened.
Breathing Techniques Pursed-Lip Breathing:
- Clears trapped air, reduces breathlessness
- Diaphragmatic/Belly Breathing: Strengthens respiratory muscles
- Steam & Humidification: Keeps airways moist and reduces irritation
Monitoring:
- Watch for persistent cough, chest tightness, breathlessness
- Regular physician visits if you live in a high-pollution city
- Annual lung-function tests (especially for children & elderly)
- Treat chronic exposure like you would treat a chronic infection: protect, fortify, monitor.
Outdoor Strategies:
- Avoid walking/exercising near main roads
- Choose parks/green belts for movement
- Keep car windows closed in traffic
- Avoid early morning & late night outdoor time in winter
- Never burn leaves, plastic, or household waste
When AQI Crosses 300 (Emergency Mode)
If AQI >300, the risk of air pollution and premature death rises significantly.
Do this immediately:
- Shift all workouts indoors
- Mandatory masks for everyone leaving the house
- Purifiers ON 24×7 in sleeping areas
- Keep children, seniors, and asthmatics strictly indoors
- Increase antioxidants and hydration
For more practical ways to protect yourself, check out Luke’s 101 free personal guide to easy breathing.
When to Consult a Doctor or Pulmonologist
Air pollution–related inflammation often stays silent, which is why early medical attention is key to preventing long-term damage and reducing the risk of air pollution–related premature death.
See a doctor if you notice:
- Persistent cough (>2–3 weeks)
- Breathlessness, chest tightness, or wheezing
- Symptoms that worsen on high-AQI days
- Recurrent throat or sinus irritation
- Frequent colds or infections (2–3+ per year)
High-risk groups who should consult early:
- Children, the elderly, and pregnant women
- Anyone with asthma, COPD, heart disease, diabetes, or low immunity
Red-flag signs (seek urgent care):
- Sudden breathlessness
- Chest pain
- Blue lips or fingertips
- Confusion or severe fatigue
Recommended tests (as advised):
- Spirometry, FeNO, chest imaging, pulse oximetry
Early evaluation helps detect airway inflammation before it progresses — and can significantly lower long-term risk.
Take charge of your health despite environmental challenges.
👉 Join our personalised Wellness Program
The Last Word
We cannot always control the air outside, but we can control how intelligently we respond to it. Air pollution is no longer just an environmental issue — it is a daily health challenge silently driving inflammation, weakening our organs, and increasing the risk of premature death.
But awareness is power. Even small, consistent actions—clean indoor air, the right food, mindful breathing, and medical guidance when needed—can protect our lungs and extend our healthy years.
Your body is engineered to heal and protect you, but it needs the right environment to do its job.
Clean air is a fundamental right, but until our cities change, our lifestyle becomes our shield. Protect your breath. Protect your life.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your nutrition, lifestyle, or healthcare regimen, especially if you have existing medical conditions or are taking prescribed medications.
Struggling with the effects of polluted air on your energy, breathing, or overall health?
We’re here to help YOU find a way.
Set up a one-on-one consultation with our team or explore our Wellness Programs to optimize your lifestyle goals.
Reach out to us at 1800 102 0253 or write to us at consults@lukecoutinho.com.

Team Luke
Start Your Wellness Journey
Feeling inspired to take the next step in your wellness journey? Connect with us to explore how our tailored programs can support your health journey. Your transformation is just a conversation away.



